DevOps Change Management in Enterprise IT Systems
What is DevOps Change Management?
DevOps Change Management is a structured process that ensures updates, configurations, and modifications in IT systems are implemented reliably and securely. In enterprise IT systems, change management coordinates software deployments, infrastructure updates, and system configurations across development, testing, and production environments. It balances agility with stability, aiming to minimize service disruptions while enabling continuous delivery. Professionals often learn these processes through structured programs such as azure devops training for beginners, which provide foundational understanding of version control, automated deployments, and workflow orchestration.
In large organizations, unregulated changes can cause outages, data inconsistencies, or security vulnerabilities. DevOps change management addresses these challenges by integrating planning, automation, and monitoring within agile workflows.
How Does DevOps Change Management Work in Real-World IT Projects?
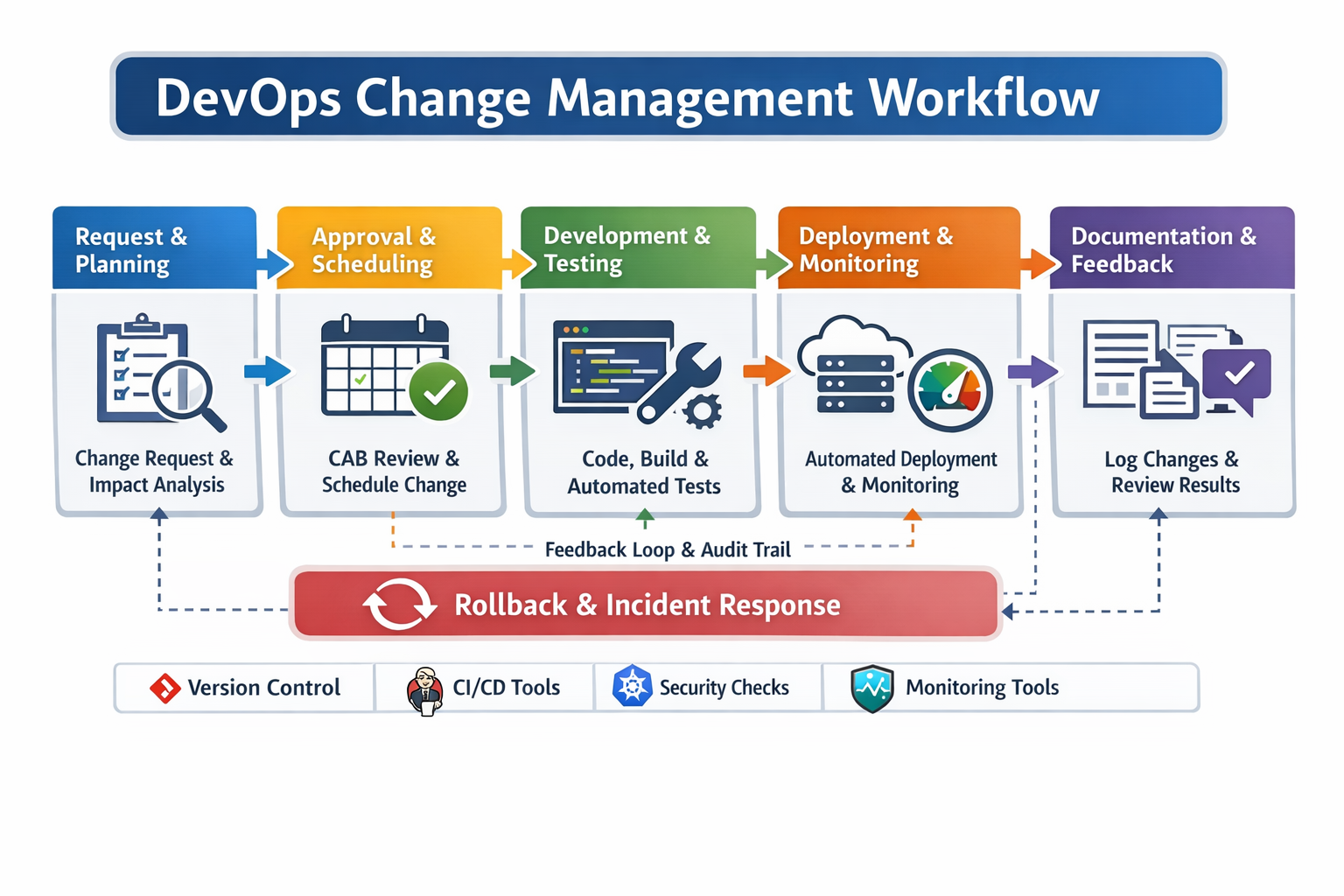
In enterprise IT environments, DevOps change management is implemented through automated pipelines, policy enforcement, and collaboration across multiple teams. The process typically involves the following stages:
-
Request and Planning:
-
Changes are submitted through tools like Jira, ServiceNow, or Azure Boards.
-
Impact analysis is performed, assessing risk, affected components, and rollback strategies.
Approval and Scheduling:
-
Change Advisory Boards (CABs) may approve high-risk changes, though many teams rely on automated approvals for low-risk updates.
-
Deployment windows are scheduled to minimize impact on business-critical services.
Development and Testing:
-
Developers implement changes in isolated branches using Git or other version control systems.
-
Continuous Integration (CI) pipelines run automated unit, integration, and regression tests.
Deployment and Monitoring:
-
Continuous Deployment (CD) tools such as Jenkins, GitHub Actions, Azure DevOps Pipelines, or AWS CodePipeline automate deployments.
-
Monitoring solutions (Prometheus, CloudWatch, or Application Insights) track performance, availability, and anomalies post-deployment.
Documentation and Feedback:
-
All changes are logged, including deployment time, approval status, and test results.
-
Feedback loops ensure lessons learned inform future change processes.
Example Workflow Table
|
Stage |
Tools / Platforms |
Key Tasks |
|
Request & Planning |
Jira, ServiceNow, Azure Boards |
Submit change request, impact analysis |
|
Approval & Scheduling |
CAB, automated workflows |
Risk assessment, deployment scheduling |
|
Development & Testing |
Git, Jenkins, Azure Pipelines |
Code changes, unit/integration tests |
|
Deployment & Monitoring |
AWS CodePipeline, CloudWatch |
Automated deployment, monitoring alerts |
|
Documentation & Feedback |
Confluence, SharePoint |
Logging, lessons learned, process updates |
Why is DevOps Change Management Important for Working Professionals?
Change management in DevOps is critical for several reasons:
-
Minimizes Risk: Reduces the likelihood of downtime or failures during deployments.
-
Supports Compliance: Helps organizations meet regulatory and audit requirements.
-
Promotes Collaboration: Aligns development, operations, and security teams in a shared workflow.
-
Enables Continuous Delivery: Supports faster releases without sacrificing system stability.
For IT professionals, mastering DevOps change management ensures career readiness for roles in release management, cloud operations, and site reliability engineering (SRE).
What Skills Are Required to Learn AWS DevOps / Azure DevOps?
To effectively implement change management in enterprise IT, professionals should develop a combination of technical, analytical, and soft skills:
Technical Skills
-
Version Control: Git, Bitbucket, or TFS
-
CI/CD Pipelines: Jenkins, Azure DevOps Pipelines, AWS CodePipeline
-
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Terraform, AWS CloudFormation, Azure Resource Manager
-
Containerization & Orchestration: Docker, Kubernetes
-
Monitoring & Logging: Prometheus, Grafana, CloudWatch, ELK Stack
Analytical Skills
-
Risk assessment and impact analysis
-
Root cause analysis for post-deployment failures
-
Understanding dependency mapping across complex systems
Soft Skills
-
Cross-team communication
-
Documentation and reporting
-
Agile collaboration
A structured azure devops course syllabus typically integrates these skills through hands-on labs, project simulations, and scenario-based exercises.
How is DevOps Change Management Used in Enterprise Environments?
Enterprise IT environments often operate across multiple cloud providers, data centers, and geographies. DevOps change management is applied in several ways:
-
Multi-Environment Deployments:
Changes are propagated from development to staging and production using automated pipelines to ensure consistency. -
Security Integration (DevSecOps):
Security checks such as vulnerability scans and compliance validations are automated as part of the deployment process. -
Automated Rollbacks:
Versioned releases enable automatic rollback in case of failure, reducing downtime and manual intervention. -
Continuous Monitoring & Feedback:
Real-time dashboards alert operations teams of anomalies, and metrics are fed back into the CI/CD process to improve future deployments. -
Cross-Team Collaboration:
Integrating development, operations, security, and quality assurance teams ensures alignment on change approvals, testing, and deployment strategies.
Tools Commonly Used in DevOps Change Management
|
Tool Category |
Examples |
Enterprise Use Case |
|
Version Control |
Git, Bitbucket, Azure Repos |
Branching, merging, rollback strategies |
|
CI/CD Pipelines |
Jenkins, Azure DevOps Pipelines, CodePipeline |
Automated build, test, and deployment |
|
Change Request Management |
Jira, ServiceNow, Azure Boards |
Logging, approvals, audit trails |
|
Infrastructure as Code |
Terraform, CloudFormation, ARM Templates |
Consistent provisioning and updates |
|
Monitoring & Logging |
Prometheus, Grafana, CloudWatch, ELK Stack |
Detecting issues post-deployment |
|
Security & Compliance |
SonarQube, Aqua Security, Checkov |
Static analysis, policy compliance |
Common Challenges in Enterprise DevOps Change Management
-
Complex Dependency Mapping: Multi-tier applications may have interdependent services that complicate deployments.
-
Cultural Resistance: Teams may resist adopting standardized processes over ad-hoc workflows.
-
Tool Integration: Ensuring CI/CD, monitoring, and ticketing systems work seamlessly requires careful planning.
-
Change Volume: High frequency of updates can overwhelm traditional approval processes.
-
Compliance Constraints: Highly regulated industries demand strict audit trails and automated controls.
What Job Roles Use DevOps Change Management Daily?
Professionals across multiple IT roles interact with DevOps change management:
|
Role |
Responsibilities Related to Change Management |
|
DevOps Engineer |
Implement CI/CD pipelines, automate deployments |
|
Release Manager |
Approve, schedule, and track software releases |
|
Site Reliability Engineer |
Monitor performance and ensure system stability |
|
Cloud Operations Engineer |
Provision infrastructure and manage IaC updates |
|
Security Engineer (DevSecOps) |
Integrate security checks into CI/CD pipelines |
What Careers Are Possible After Learning AWS DevOps / Azure DevOps?
Professionals trained in DevOps change management can pursue careers such as:
-
DevOps Engineer
-
Cloud Engineer (AWS / Azure)
-
Release Manager
-
Site Reliability Engineer (SRE)
-
Automation Specialist
-
DevSecOps Specialist
Hands-on knowledge from AWS DevOps/DevSecOps Training programs equips professionals to implement enterprise change management workflows, automate deployments, and integrate security and compliance checks efficiently.
FAQ / Q&A
Q1: What is the difference between DevOps change management and ITIL change management?
A1: DevOps change management emphasizes automation, continuous delivery, and collaborative workflows. ITIL change management is process-heavy, often manual, and structured around formal approvals. Both aim to reduce risk, but DevOps integrates changes into agile CI/CD pipelines.
Q2: Can change management slow down deployment speed?
A2: Traditional manual processes can create bottlenecks. In DevOps, automation, automated approvals, and CI/CD pipelines ensure change management supports rapid releases while maintaining stability.
Q3: How is change risk assessed in DevOps?
A3: Risk assessment considers service impact, dependencies, rollback options, and test coverage. Automated tools, monitoring, and version control improve risk visibility.
Q4: Which DevOps tools are essential for beginners?
A4: Beginners should focus on Git, Jenkins or Azure DevOps Pipelines, Docker, and Terraform. Structured azure devops training for beginners programs cover these essentials with hands-on labs.
Q5: How does DevSecOps relate to change management?
A5: DevSecOps integrates security into the DevOps pipeline. Automated security checks, compliance validations, and vulnerability scanning become part of the change management process.
Best Practices for Effective DevOps Change Management
-
Automate approval workflows for low-risk changes.
-
Implement consistent versioning for application and infrastructure components.
-
Use feature flags to enable controlled releases.
-
Integrate security testing within the CI/CD pipeline.
-
Maintain detailed logs for auditing and rollback purposes.
-
Encourage cross-team collaboration and communication.
Real-World Example: Enterprise Change Workflow
Scenario: Deploying a new microservice in a multi-cloud environment.
Steps:
-
Developer commits code to Git repository.
-
Jenkins pipeline runs unit and integration tests.
-
Terraform provisions required infrastructure in AWS and Azure.
-
Automated security scans validate configurations.
-
Azure DevOps Pipelines deploy the service to staging.
-
Prometheus monitors performance; errors trigger rollback if thresholds exceeded.
-
Deployment logs are archived in Confluence for audit.
This workflow ensures minimal downtime, compliance adherence, and cross-team coordination.
Key Takeaways
-
DevOps change management ensures reliable, secure, and traceable updates in enterprise IT systems.
-
Automation, CI/CD pipelines, and monitoring are core components.
-
Tools like Git, Jenkins, Azure DevOps, Terraform, and CloudWatch are industry standards.
-
Professionals benefit from learning structured skills through azure devops course syllabus and hands-on labs.
-
Career paths include DevOps Engineer, SRE, Cloud Operations Engineer, and DevSecOps Specialist.
Explore H2K Infosys courses today to gain practical experience in AWS DevOps and DevSecOps, and build a career-ready skillset.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jeux
- Gardening
- Health
- Domicile
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Autre
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness