Understanding TOSCA Modules and Reusable Components
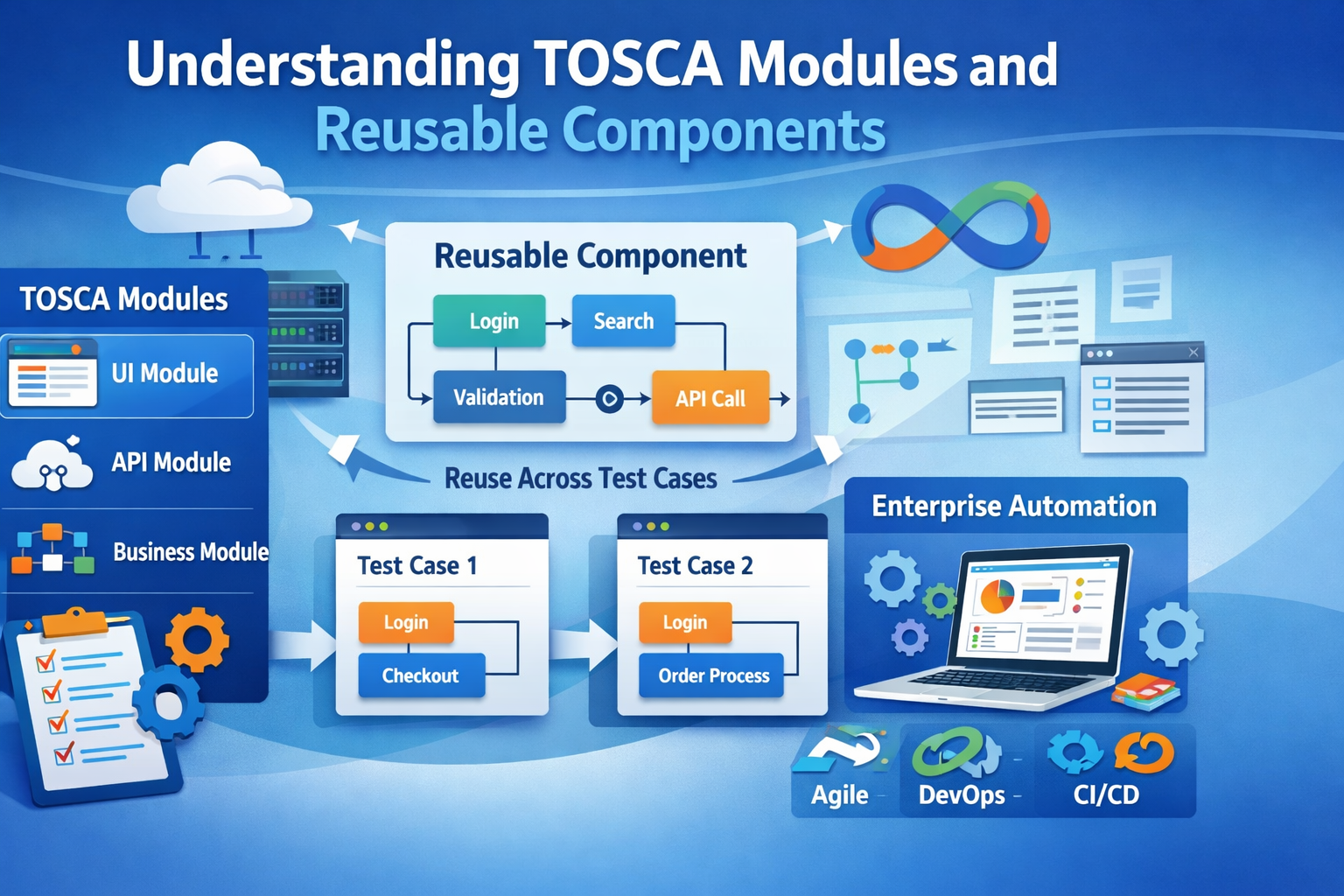
TOSCA Modules and reusable components are structured building blocks in Tricentis TOSCA that allow automation teams to design, maintain, and scale test cases efficiently by separating technical elements, business logic, and test data. These concepts are a core focus in Tricentis TOSCA Certification Online, as they support model-based test automation, where changes in applications are managed centrally and reused across multiple test scenarios. This approach is commonly used in enterprise test automation strategies to reduce maintenance effort and improve test reliability.
What is Understanding TOSCA Modules and Reusable Components?
In TOSCA, a Module is a container that represents a logical grouping of test artifacts, such as application screens, controls, APIs, or business flows. A reusable component is a test element or test step that can be designed once and used across multiple test cases without duplication.
Together, these concepts form the backbone of model-based automation, a methodology where:
-
The technical model represents the application under test.
-
The test cases reference this model instead of hard-coded scripts.
-
Updates to the application are reflected by modifying the model, not rewriting every test.
This structure is central to tosca automation testing in enterprise environments, where large applications change frequently and test coverage must remain stable across releases.
How Does TOSCA Training Work in Real-World IT Projects?
In professional environments, TOSCA Training typically focuses on aligning automation practices with software delivery workflows such as Agile, DevOps, and CI/CD pipelines. The use of modules and reusable components is introduced early because it directly affects long-term project maintainability.
Typical Enterprise Workflow
-
Application Analysis
Test architects analyze the application structure (web, desktop, API, or mobile). -
Module Creation
UI elements, API endpoints, or services are scanned and stored in TOSCA Modules. -
Business Logic Design
Common workflows (login, order creation, approval flows) are built as reusable components. -
Test Case Assembly
Testers combine components to form end-to-end scenarios. -
Execution and Reporting
Tests run through TOSCA ExecutionLists and integrate with CI tools.
Integration with IT Toolchains
In production environments, TOSCA is often connected to:
-
CI/CD Tools: Jenkins, Azure DevOps, GitLab
-
Test Management: Jira, qTest, ALM
-
Version Control: Git-based repositories
-
Defect Tracking: Jira, ServiceNow
Modules allow automation assets to be versioned and managed consistently across teams and environments.
Why Are TOSCA Modules Important for Working Professionals?
For IT professionals, the value of modules lies in how they support collaboration, scalability, and maintenance.
Practical Benefits
-
Reduced Maintenance Effort
When an application UI changes, teams update the module instead of editing hundreds of test cases. -
Team Collaboration
Automation engineers, manual testers, and business analysts can work on different layers of the same model. -
Consistency Across Projects
Shared components ensure standard workflows behave the same in regression, UAT, and production validation. -
Audit and Compliance Support
Centralized test assets make it easier to demonstrate coverage for regulated industries such as banking, healthcare, and insurance.
These factors explain why modular automation approaches are commonly emphasized in professional TOSCA Training programs.
How Is TOSCA Used in Enterprise Environments?
Large organizations often test complex systems that include multiple technologies and integrations. TOSCA Modules provide a way to manage this complexity.
Common Enterprise Use Cases
-
ERP Testing (SAP, Oracle)
Modules represent transactions, fields, and workflows across finance, HR, and supply chain systems. -
Web and Mobile Applications
UI elements are scanned into modules for responsive testing across browsers and devices. -
API and Microservices Testing
Services and endpoints are stored as reusable technical modules. -
End-to-End Business Processes
Cross-system workflows are built using reusable components that span UI, API, and backend layers.
Deployment Context
In enterprise setups, TOSCA environments often include:
-
Centralized repositories for modules
-
Role-based access control for test assets
-
Integration with release management systems
-
Execution environments across multiple test environments (QA, staging, pre-production)
What Are TOSCA Modules?
A TOSCA Module is a structured representation of the application under test. It contains the technical definition of how TOSCA interacts with the system.
Types of Modules
|
Module Type |
Purpose |
Example Use |
|
UI Modules |
Represent screens and controls |
Web forms, desktop windows |
|
API Modules |
Represent service endpoints |
REST or SOAP services |
|
Business Modules |
Represent workflows |
Order processing, approvals |
|
Database Modules |
Represent data structures |
Tables, queries |
Module Structure
A module typically includes:
-
Attributes: Technical identifiers for elements
-
Controls: Buttons, fields, links, services
-
Properties: Metadata such as type and validation rules
This structure allows test cases to interact with applications through the model rather than direct scripting.
What Are Reusable Components in TOSCA?
Reusable components are standardized sequences of test steps that perform a specific function. They are stored separately and referenced by multiple test cases.
Examples of Reusable Components
-
User login process
-
Product search and selection
-
Data validation routines
-
API authentication flow
-
Environment setup steps
Why Reusability Matters
In professional testing environments:
-
Teams avoid duplication of logic
-
Updates propagate automatically
-
Test cases remain readable and maintainable
This design aligns with software engineering principles such as DRY (Don’t Repeat Yourself) and modular design.
How Do Modules and Reusable Components Work Together?
Modules define what the system looks like, while reusable components define what the system does.
Workflow Example
-
A UI module stores the login screen fields and buttons.
-
A reusable component references that module to perform login.
-
Multiple test cases call the login component.
-
If the login page changes, only the module is updated.
This separation is a core principle in tosca automation testing and supports long-term automation scalability.
Step-by-Step: Creating a Basic TOSCA Module
Step 1: Scan the Application
Use TOSCA’s scan feature to capture UI or API elements.
Step 2: Organize Controls
Group fields, buttons, and services logically within the module.
Step 3: Define Attributes
Set technical identifiers and validation rules.
Step 4: Save to Repository
Store the module in a shared workspace for team access.
Step-by-Step: Building a Reusable Component
Step 1: Identify Common Workflow
Choose a process used in multiple tests, such as authentication.
Step 2: Reference Relevant Modules
Link the component to the appropriate UI or API modules.
Step 3: Parameterize Data
Allow input values to be passed dynamically.
Step 4: Test Independently
Validate the component before integrating into test cases.
How Is TOSCA Training Aligned with Industry Practices?
Professional training programs often align with:
-
Agile Testing Principles
-
DevOps Automation Strategies
-
Risk-Based Testing Models
-
Continuous Testing Pipelines
Learning Path Example
|
Phase |
Focus Area |
Outcome |
|
Foundation |
Module design |
Understand application modeling |
|
Intermediate |
Component reuse |
Build scalable test flows |
|
Advanced |
CI/CD integration |
Automate release validation |
|
Professional |
Governance |
Manage test assets across teams |
What Skills Are Required to Learn TOSCA Training?
Technical Skills
-
Basic software testing concepts
-
Understanding of web and API technologies
-
Data handling and parameterization
Professional Skills
-
Test design thinking
-
Process documentation
-
Collaboration in cross-functional teams
These skills are typically developed progressively in structured training and on-the-job projects.
What Job Roles Use TOSCA Daily?
|
Role |
How TOSCA Is Used |
|
Automation Engineer |
Builds modules and components |
|
QA Analyst |
Executes and validates test cases |
|
Test Architect |
Designs automation framework |
|
DevOps Engineer |
Integrates tests into CI/CD |
|
Business Analyst |
Validates workflows |
What Careers Are Possible After Learning TOSCA Training?
Professionals trained in TOSCA often move into roles such as:
-
Automation Consultant
-
Quality Engineering Lead
-
Test Automation Architect
-
DevOps Quality Specialist
-
Enterprise QA Manager
These roles typically involve strategic decision-making around automation frameworks and quality governance.
How Does TOSCA Support Scalability and Performance?
Enterprise Constraints
-
Large test suites
-
Distributed teams
-
Multiple environments
-
Regulatory requirements
TOSCA Design Advantages
-
Centralized updates
-
Role-based access
-
Version-controlled modules
-
Parallel execution support
These features help teams manage automation at scale.
Tool Comparison: TOSCA vs Script-Based Automation
|
Feature |
TOSCA |
Script-Based Tools |
|
Maintenance |
Centralized |
Distributed |
|
Learning Curve |
Moderate |
High |
|
Reusability |
Built-in |
Custom |
|
Scalability |
High |
Variable |
|
Collaboration |
Structured |
Code-based |
Common Challenges Teams Face
-
Poor module organization
-
Overly complex components
-
Lack of naming standards
-
Insufficient documentation
-
Inconsistent version control
Best Practices
-
Use clear naming conventions
-
Maintain module hierarchies
-
Document component logic
-
Review assets regularly
How Tricentis TOSCA Certification Online Fits Into Professional Development
Certification programs typically validate:
-
Understanding of model-based automation
-
Module and component design
-
Integration with enterprise toolchains
-
Test management and governance
These certifications are often used as benchmarks for automation proficiency in large organizations.
FAQ: TOSCA Modules and Reusable Components
What is a TOSCA Module in simple terms?
A module is a digital model of an application’s technical elements that allows tests to interact with the system without hard-coding actions.
Can reusable components work across different projects?
Yes, if applications share similar workflows or standards, components can be adapted and reused with minimal changes.
Is coding required for TOSCA automation testing?
TOSCA is primarily no-code, but technical understanding improves how effectively modules and components are designed.
How do modules help in Agile projects?
They allow quick updates to tests when application changes occur, supporting frequent releases.
What industries commonly use TOSCA?
Banking, healthcare, retail, manufacturing, and enterprise software providers often use model-based automation tools.
Key Takeaways
-
TOSCA Modules represent the technical structure of applications.
-
Reusable components define standardized business workflows.
-
Together, they enable scalable and maintainable automation.
-
This approach supports enterprise testing, CI/CD integration, and compliance needs.
-
Structured TOSCA Training helps professionals align automation skills with real-world IT environments.
To gain hands-on experience with model-based automation and reusable test design, explore structured learning paths at H2K Infosys that focus on practical TOSCA workflows and enterprise testing practices.
Their courses are designed to help working professionals apply these concepts in real project environments and long-term career development.

- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Игры
- Gardening
- Health
- Главная
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Другое
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness