The Complete Guide to Industrial Packaging Machines: Revolutionizing Product Protection and Distribution
In today's highly competitive manufacturing environment the effectiveness of packaging for products directly affects business profits as well as supply chain efficiency and the satisfaction of customers. Packaging machines have advanced from manual processes to advanced automated systems that manage millions of items every day across a variety of industries. Knowing what packaging machines are and how they work, and the applications they serve is crucial for any business seeking to maximize production lines while maintaining competitive edge in today's market.
Understanding Packaging Machinery: The Foundation of Modern Production
Packaging machines are an automatic or semi-automated device designed to wrap the, protect, or contain and then prepare the product to be stored, distributed sales, and final use. These machines in the industrial sector perform a variety of processes like packing, sealing, filling labels, palletizing, and wrapping products with accuracy and precision that is much greater than the manual capabilities. from food processing establishments to pharmaceutical labs Chemical plants, to warehouses for consumer goods packaging equipment acts as the vital link between market supply and manufacturing.
The primary reason for packaging machinery is beyond the simple confinement. They ensure the integrity of products throughout transportation, prolong shelf life by sealing it with hermetic and provide security features that are tamper-proof display branding and other regulatory information, and allow for efficient handling across the entire logistics chain. Modern packaging automation is essential for companies looking to cut costs on labor as well as reduce material waste. ensure consistency in quality and expand operations to meet the growing demand from the market.
The Mechanical Architecture Behind Packaging Systems
Packaging machines function by integrating mechanical, electrical and pneumatic components that work in sync. They are at the heart of these systems usually have feeding mechanisms that bring items to the packing line in precisely controlled speeds. Conveyor systems transfer products to multiple stations where different packaging operations are carried out continuously. The systems of vision and sensor technology determine the location of the item, confirm its integrity and assure an accurate position all through the procedure.
Control systems are the brains for modern equipment used in packaging. The Programmable Logic Controls (PLCs) are able to coordinate time sequences and manage speed parameters, check operational metrics and take corrections when errors are observed. Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs) provide users with intuitive touchscreen controls to manage recipes production tracking, recipe management, and diagnosing troubleshooting issues. Modern machines include motors with servos to ensure precise positioning, pneumatic actuators that allow swift movement, and load cells to ensure accurate weight measurements.
Material handling equipment varies depending on the particular packaging type, but typically include unwinding equipment that allow flexible packaging hopper assemblies to facilitate large-scale product dispensing as well as robotic pick-and-place devices for precise arrangement of products. Sealing systems use Ultrasonic vibration, heat, or the application of adhesive to create safe closures. Cutting devices with guillotine or rotary blades are used to separate packagings from continuous streams of material with a repeatable precision.
Diverse Categories of Packaging Equipment
The packaging machinery world encompasses various types of equipment that are specialized that are designed to meet specific purposes and characteristics of the product. Form-fill-seal machines are among the most flexible categories. They are capable of creating packaging from flat roll stock, by shaping an empty container and filling it up with product, then sealing it with an ongoing process. These systems are the most popular in the food industry with snacks, food and coffee, as well as spices and liquids packaged in pouches.
Filling machines are a different category that is specifically designed to precisely disperse items into containers that are pre-formed. Liquid fillers deal with liquids, oils, chemical and pharmaceuticals by using gravimetric, volumetric or flow meter techniques. Powder filling equipment is used to handle dry materials such as flour, protein supplements cement, as well as industrial chemicals. A leading manufacturer of a packaging machine with a focus on filling technology has to take into consideration specific characteristics of the product like viscosity particles' size and density and flow properties when creating specifications for the equipment.
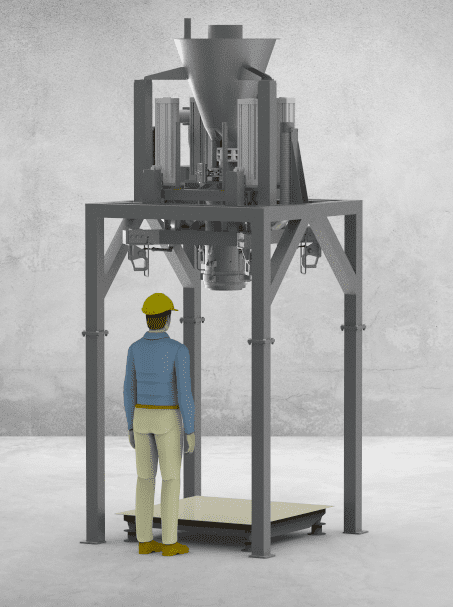
Jumbo bags filling machines systems are high-performance equipment specifically designed to handle bulk materials in industrial settings. These sturdy machines are able to fill large versatile intermediate bulk containers (FIBCs) with a variety of products from agricultural products to chemicals, construction materials and plastic resins. They can hold from 500-2000 kilograms per bag, and include advanced weighing systems that guarantee the accuracy of the weighing within a tight range despite the huge quantities of material involved. It includes dust containment systems that are automated, device for bag attaching, densification to maximising payload as well as integrated conveyors to ensure the most efficient removal of bags.
Cartoning equipment automatizes the procedure of creating cardboard cartons, adding products and closing flaps with accuracy. They handle the essential packaging needs for cosmetics, pharmaceuticals foods, and consumer products. Palletizers and case packers work laterally, placing primary packaging into corrugated shipping containers and then arranging the cases on pallets to be delivered by distribution centers.
The paper bag valve filling equipment provides industries with eco-friendly packaging solutions for granular and powdered products. These fillers are specially designed to insert products through a valve in multi-wall paper bags that are commonly used to store cement flour animal feed, chemicals and other building materials. The valve bag design provides better dust control, speedier filling cycles, and self-sealing capabilities which eliminate the requirement for separate closure procedures. The latest valve bags include air evacuation systems and vibration platforms to aid in product settling, and automatic bag placement systems that simplify large-scale operations.
Industry Applications Across Manufacturing Sectors
The food and drink industry is the largest user of packaging equipment that can be used for applications ranging from farm-fresh products to processed convenience food. Bakeries utilize flow wrappers for bakery and other pastry items while dairy facilities use aseptic filling equipment for extending shelf-life yogurt and milk. Meat processors use vacuum packaging equipment that eliminates oxygen to avoid spoilage, and beverage companies have high-speed bottling lines that are capable of filling thousands of containers every hour. The compliance with food safety regulations, hygiene standards and traceability requirements drive the continuous development of Food packaging techniques.
Pharmaceutical manufacturing requires the highest precision and hygiene standards for packaging operations. Blister packaging machines create individual dose compartments to hold tablets and capsules, resulting in tamper-proof consumer packs. Stoppering and filling systems manage injectable medicines in cleanrooms. The serialization system prints unique identification numbers for each package in order to ensure compliance with the regulatory requirements to combat counterfeit drugs. The pharmaceutical producer of packaging equipment must meet the validation standards that document consistency in performance, under strict quality control systems.
The chemical and agricultural industries use specially designed packaging machinery for bulk and hazardous commodities. Drum filling systems deal with liquid chemicals by using explosive-proof electrical components as well as corrosion-resistant construction materials. Packaging and seed treatment lines cover dry, wrap, and pack agricultural products, utilizing integrated quality control systems. Fertilizer plants have automated bagging lines which fill with, weigh, sew and palletize bags of hundreds per hour, with only minimal intervention from the operator.
Consumer goods producers including household items, cosmetics electronic products, toys and other items use flexible packaging solutions for that can accommodate a variety of designs and configurations of their products. Shrink wrap machines produce rigid, transparent packaging that showcases products' features and protecting them from contamination. Skin packaging binds products to the backing of paperboard by with the help of vacuum and heat making display that is ready for retail. Fulfilment centres for online sales are increasingly deploying automation to create packaging solutions that are able to customize the size of boxes, thus reducing the cost of dimensional weight and the consumption of materials.
Technical Specifications Driving Performance
Understanding the performance metrics that matter aids businesses in selecting the most suitable packaging equipment for their specific needs. The speed ratings expressed in bags per minute or bags per hour or even cases per hour show the capacity of production. The entry-level semi-automatic equipment could be able to process between 10 and 30 packages per minute, while high-speed automation lines can process 300 to 600 packages per minute in simple applications. The large bag filling machines class typically processes between 30 and 120 bags per hour, based on the specifications of the bag and its weight.
Specifications for accuracy define the precise way machines dispense quantity targets, usually described in terms of percent deviations or variance in weight. Pharmaceutical applications need accuracy to within +-0.5 percent of the weight target in bulk filling, while bulk industrial applications may allow for +-1-2 percent tolerance. Modern load cell technology and computer algorithms allow real-time adjustments while keeping the accuracy of the product in check despite variations.
Changeover time is a crucial efficiency measure, assessing the speed at which equipment switches between various products, package sizes or formats. Quick-change designs that do not require tools motorized positioning, as well as recipes-driven automation can reduce changeover times from minutes to hours, increasing productivity and uptime. Modular design allows for reconfiguration to different packaging formats, without complete system replacement.
The parameters for flexibility indicate the range of packages and products the machine is capable of handling. Certain machines are specialized in narrow areas, which maximizes efficiency and speed for specific production, whereas flexible machines can accommodate different sizes of containers as well as product types and specifications for materials. Multi-format technology allows for future-proofing as portfolios of products change and market needs change.
Integration into the Production Line Ecosystems
Modern packaging machines are not operated as separate units, but rather in a broader production system. Upstream processes include mixing cooking, extruding or assembling feed ingredients into packaging lines with automatized transfer mechanism. Downstream operations like metal detection checking, check weighing, marking cases, labelling and palletizing finish the packaging process prior to the warehouse is stored or directly shipped.
Communication protocols enable equipment-to-equipment data exchange coordinating production flow. Industrial Ethernet networks utilizing standards like OPC-UA and MQTT send real-time production information into Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) platforms. This allows central production monitoring and scheduling of maintenance predictively and overall equipment efficiency (OEE) monitoring across several production lines.
Vision inspection systems that are integrated into packaging machines can perform quality assurance by checking for defects, such as improper seals or labels that are not present, incorrect printing codes, or damaged packaging. Reject mechanisms remove products that are not in compliance, while not halting production. Control algorithms for statistical processes examine inspection data and identify trends before problems become systematic.
Robotic integration is a growing trend as cobots (cobots) or industrial robotics manage packing orientation, product loading and packing cases. An effective paper valve bag filling machine typically integrates bags that are placed by robotic systems which remove empty pallets and place their bags onto filling outlets and then transfer the bags filled with food onto palletizing or conveyor systems. The automation eases the burden on operators and improves the consistency of cycle times.
Material Science and Packaging Innovation
The connection between packaging machinery and packaging materials requires constant advancement as new materials provide greater sustainability, function and cost effectiveness. The technology of flexible films has evolved significantly with multi-layer coextruded designs that provide barrier properties to protect products from moisture, oxygen and light, while retaining the strength of the material for processing at high speeds.
Biodegradable and compostable film made using plant-based polymers require special sealing parameters because their thermal properties are different from those of conventional plastics. Machine manufacturers work with suppliers of materials to develop heat profiles, settings for pressure and dwell times designed for the use of sustainable materials. Paper-based pouches as alternatives to plastic require adjustments to sealing and forming mechanisms that can accommodate various stiffness of materials and sensitivities.
Smart packaging that includes RFID tags, printed electronics as well as QR codes need the integration of packaging equipment as well as serialization systems. Labelers that apply and print coordinate with manufacturing data from upstream, ensuring that every package is unique and provides transparency of the supply chain from the manufacturer to end-user. Temperature-sensitive inks, freshness indicators, and tamper-evident features add functional value requiring precise application during packaging operations.
Operational Efficiency and Total Cost Optimization
The process of investing in packaging equipment involves the analysis of all costs of ownership in addition to the initial capital expense. Operating costs comprise energy consumption as well as compressed air consumption materials for maintenance, as well as labor costs for operators. Modern designs that are energy efficient and incorporate technology for servo motors as well as on-demand air compressors along with heat recovery technologies drastically lower utility costs compared with older pneumatic or hydraulic systems.
Maintenance requirements are depending on the complexity of the machine along with the production environment, as well as the level of operation. Regular maintenance programs that follow the manufacturer's recommendations can reduce unexpected downtime. The most frequent maintenance tasks include lubrication of moving parts replacing wear parts such as seal jaws, cutting blades or sealing devices testing of the weighing system and cleaning of the product contact surfaces. A well-maintained machine will provide consistent performance for a period of 15 to 20 years.
Training maintenance technicians and operators will ensure optimal utilization of equipment. A comprehensive training program covering the operation of machines, fundamental troubleshooting, changing procedures and safety protocols minimize mistakes, reduce damage and increase first-time quality. Many manufacturers offer remote technical support, videos tutorials and on-site training to ensure the competence of staff.
Reducing material waste is a important cost factor. Correctly calibrated equipment reduces giveaway (overfilling) and decreases the amount of film that is discarded during changeovers, and stops packaging defects that require rework. Modern machines include waste-tracking capabilities for finding improvement opportunities across processing.
Future Trends Shaping Packaging Automation
Machine learning and artificial intelligence applications are helping transform manufacturing equipment for packaging from non-reactive machines to proactive systems. AI algorithms analyse the data from sensors to determine optimal operating parameters that increase the efficiency of production while minimizing the chance of causing defects. Predictive maintenance systems anticipate component failures prior to breakdowns occurring by scheduling maintenance for scheduled downtime instead of unexpected interruptions to production.
Sustainable initiatives are driving the creation of equipment that can handle recycled materials, which reduces the use of energy and the use of materials. Lightweighting technology makes packages with less material, while still ensuring the highest standards of protection. Solvent-free and water-based adhesives are a better alternative to the bonding techniques that require a lot of chemicals. Equipment designed for simple removal and recycling of components extends the environmental impact of packaging to the machines.
The ability to customize and personalize your product allows for small-batch manufacturing that can meet the demand of consumers for exclusive products. Digital printing incorporated into packaging lines can produce different graphics, personal messages and limited-edition designs, without modifications to the tools that are required by traditional printing techniques. This versatility allows for regionally-specific marketing campaigns, regional customisation and direct-to-consumer models of business.
Collaborative automation combines the benefits of total automation while allowing human sagacity and judgement. Instead of replacing workers modern packaging systems enhance the capabilities of humans to handle repetitive tasks while the operators focus on quality control as well as material management along with process efficiency. This collaboration between humans and machines makes for safer, more fun workplaces while ensuring the efficiency gains.
Conclusion: Strategic Investment in Packaging Excellence
Packaging machinery is a major investment that has a direct impact on product quality performance, efficiency in operation, and the competitive position. It is whether you choose to deploy a Jumbo bag filling device for handling bulk materials or setting up a filtering device for paper bags for environmentally sustainable production of industrial packing, or choosing the right supplier of packing machine equipment for food processing the success of your project requires a thorough analysis of the production requirements and future requirements for scalability and the total costs.
The shift of manual packing to automated systems is a reflection of the broader trend in manufacturing towards sustainable development, digitalization and efficiency. Companies that embrace advanced packaging technology can be prepared for growth as they adapt rapidly to market trends and provide consistently high-quality products that meet ever-higher demands of consumers. As packaging equipment continues to advance with the advancement of robotics, artificial intelligence and environmentally sustainable materials, companies that invest in these technologies gain competitive advantages in ever-changing global markets.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jocuri
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Alte
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness



